
A quick comparison to help you choose the smarter lifting solution.
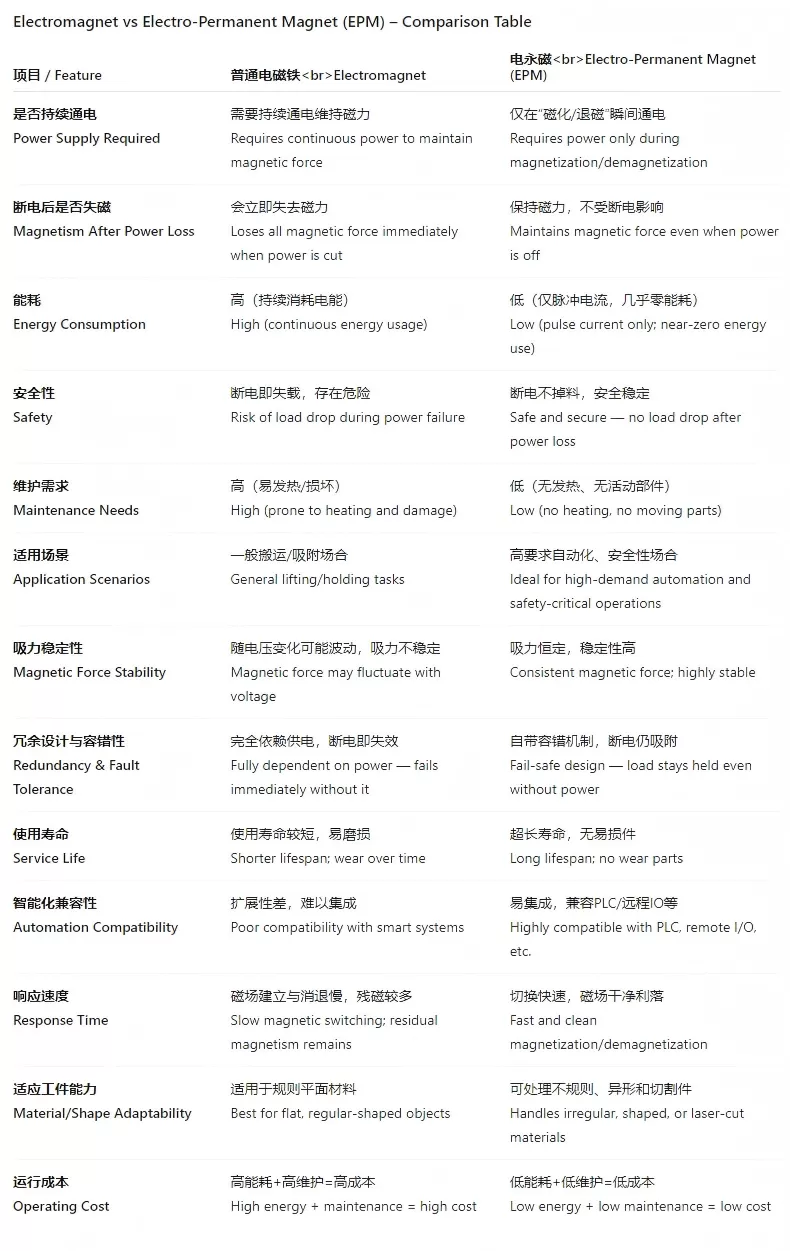
Electromagnet: Requires continuous power to maintain magnetic force
EPM: Requires power only during magnetization/demagnetization
Electromagnet: Risk of load drop during power failure
EPM: Maintains grip even during power loss — fail-safe design
Electromagnet: High (constant energy use)
EPM: Ultra-low (only pulse current needed)
Electromagnet: Prone to overheating and damage
EPM: No heat, no moving parts — minimal maintenance
Electromagnet: General-purpose lifting only
EPM: Ideal for steel plates, coils, pipes, and irregular laser-cut parts
Electromagnet: Magnetic force fluctuates with voltage
EPM: Consistent and stable force at all times
Electromagnet: High (due to energy + maintenance)
EPM: Low (energy-efficient and long-lasting)
Electromagnet: Limited integration capability
EPM: Easily integrates with PLCs, sensors, and smart systems
Attn: Ian Yi
Mob: 8618974071177 (Wechat/ WhatsApp)
Email: [email protected]
Address: 101 room, 16 Building, LIANDO U VALLEY, No.36 Zhongke Road, Economic and Technological Development Zone, Yueyang City, Hunan Province, China